Adapting Functional Exercises for Different Abilities

Assessing Individual Needs and Limitations
Identifying Physical Limitations
A crucial first step in adapting functional exercises is identifying any physical limitations that might impact an individual's ability to perform the exercises safely and effectively. These limitations could range from injuries, such as a recent knee sprain, to chronic conditions like arthritis or osteoporosis. Understanding the specific limitations is essential to modifying exercises, ensuring proper form, and preventing further injury or exacerbating existing conditions. Thorough assessment of range of motion, strength, balance, and flexibility is paramount in this process.
Careful observation and dialogue with the individual are key. Asking about past injuries, current pain points, and any limitations in movement is vital. This information, combined with a physical assessment, allows for a personalized approach to exercise modification.
Considering Cognitive and Sensory Factors
Functional exercises aren't just about physical capabilities; cognitive and sensory factors also play a significant role. Individuals with cognitive impairments, such as memory problems or processing delays, may require different approaches to learning and executing exercises. For example, a clear, step-by-step demonstration and repetitive practice might be necessary to ensure understanding and successful execution.
Sensory limitations, such as reduced vision or hearing, may necessitate modifications to the exercise environment or the way instructions are delivered. Using visual cues, auditory feedback, or tactile guidance can help individuals with sensory impairments effectively participate in functional exercises.
Tailoring Exercise Intensity and Duration
Adapting functional exercises also involves adjusting the intensity and duration of the exercises to suit the individual's needs. For those with lower fitness levels, starting with shorter durations and gradually increasing the duration and intensity over time is essential. This progressive overload approach allows the body to adapt without causing undue stress or injury. Careful monitoring of the individual's response to exercise is important, ensuring they don't experience excessive fatigue or discomfort.
Conversely, individuals with higher fitness levels might require more challenging variations or longer durations to maintain a progressive challenge. This tailoring ensures the exercise remains effective and promotes consistent progress.
Modifying Exercise Technique and Equipment
Often, adapting functional exercises involves modifying the technique and using appropriate equipment. Modifications might include using lighter weights, altering the range of motion, or adjusting the exercise's stance or posture. For example, exercises that involve deep squats might need to be modified to a seated squat or a chair squat for individuals with balance or joint issues.
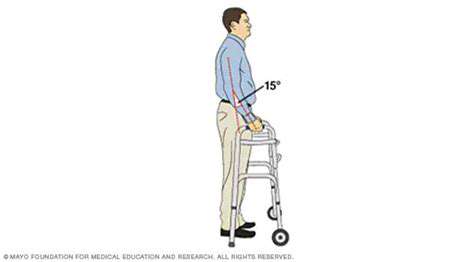
Utilizing assistive devices, such as handrails or stability balls, can also aid in adapting exercises for individuals with specific needs. Proper equipment selection and usage can significantly impact the safety and effectiveness of the exercise routine.
Creating a Personalized Exercise Progression
Developing a personalized exercise progression is key to ensuring that the adaptation process is effective and sustainable. The progression must be tailored to the specific individual's needs and limitations, taking into account their physical and cognitive abilities. This customized approach allows for gradual improvement and prevents frustration or burnout.
Regular monitoring and evaluation of progress are crucial. Adjustments to the exercise plan should be made based on the individual's response and feedback. This iterative process ensures that the exercises remain challenging and motivating, while also remaining safe and effective.
Utilizing Assistive Equipment and Modifications
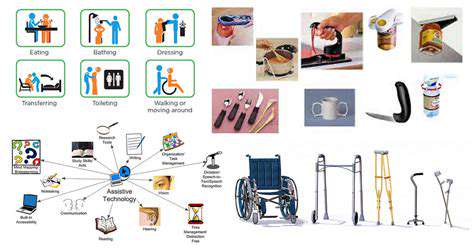
Choosing the Right Assistive Equipment
Selecting the appropriate assistive equipment is crucial for maximizing independence and accessibility. Careful consideration must be given to the specific needs and limitations of the individual. This involves not only evaluating physical capabilities but also considering cognitive abilities and environmental factors. Understanding the features and functionalities of different types of equipment is essential for making informed decisions. A thorough assessment conducted by a qualified professional can provide invaluable guidance in this process.
Factors like the type of activity, the desired outcome, and the user's comfort level should all play a role in the decision-making process. This is not a one-size-fits-all approach; tailoring the equipment to individual needs is key to its effective use. Consulting with therapists and other specialists can lead to a more personalized and successful outcome.
Understanding Equipment Functionality
Knowing how to operate and maintain assistive equipment is vital for its effective use. This includes understanding the different controls, settings, and safety features. Detailed instructions and training are often provided with the equipment, but seeking additional clarification from professionals or support groups can be invaluable. Proper maintenance is critical to ensuring the longevity of the equipment and its optimal performance.
Implementing Equipment into Daily Routine
Integrating assistive equipment into daily routines can seem challenging at first, but with proper planning and support, it can become seamless and integrated. Strategies for gradual implementation and practice are key to successfully incorporating these tools into everyday tasks. Identifying potential challenges and proactively addressing them will help streamline the transition. This might involve modifying existing routines or creating new habits.
Creating a supportive environment for using the equipment can also make a significant impact. This support could come from family members, caregivers, or peers. Clearly outlining responsibilities and expectations for using the equipment can also contribute to success. Consideration should also be given to the potential impact on social interactions and activities.
Addressing Potential Challenges
Implementing assistive equipment can present various challenges, ranging from initial setup to ongoing maintenance and troubleshooting. Understanding these potential obstacles in advance can help to mitigate their impact. Unexpected technical difficulties or user errors can be frustrating, but anticipating these issues can facilitate a more proactive approach to problem-solving. Having a support network in place, whether through professionals or peer groups, can be invaluable.
Maintenance and Care of Assistive Equipment
Maintaining the proper care and upkeep of assistive equipment is crucial for ensuring longevity and optimal functionality. Regular cleaning, servicing, and troubleshooting can prevent premature wear and tear and extend the life of the equipment. This can involve following manufacturer guidelines, performing routine checks, and seeking professional maintenance when needed. Regular checks can help prevent breakdowns and maintain a high level of performance. Understanding the specific needs of each piece of equipment is essential for its proper maintenance.
Maximizing Independence with Assistive Equipment
The ultimate goal of utilizing assistive equipment is to maximize independence and self-sufficiency. This involves adapting routines, tasks, and environments to accommodate the use of the equipment. Successfully incorporating assistive technology can significantly improve quality of life. It fosters a greater sense of control and autonomy in daily life. By working collaboratively with healthcare providers, therapists, and support systems, individuals can achieve their desired level of independence and participation.