Balance Exercises for Seniors 65 70 to Prevent Falls
Incorporating Balance Exercises into Daily Activities

Benefits of Incorporating Balance Exercises
Improving balance is crucial for overall well-being, reducing the risk of falls, and enhancing physical function, particularly as we age. Regular balance exercises can significantly improve stability and coordination, enabling us to navigate daily activities with greater confidence and ease. These exercises are not just for the elderly; people of all ages can benefit from incorporating balance training into their routine.
Balance exercises are a fantastic way to build strength in the muscles that support your body, thereby decreasing the likelihood of falls and injuries. They also improve proprioception, which is the body's awareness of its position in space. This heightened awareness can lead to better posture and reduced risk of falls, especially important in maintaining independence as we age.
Types of Balance Exercises
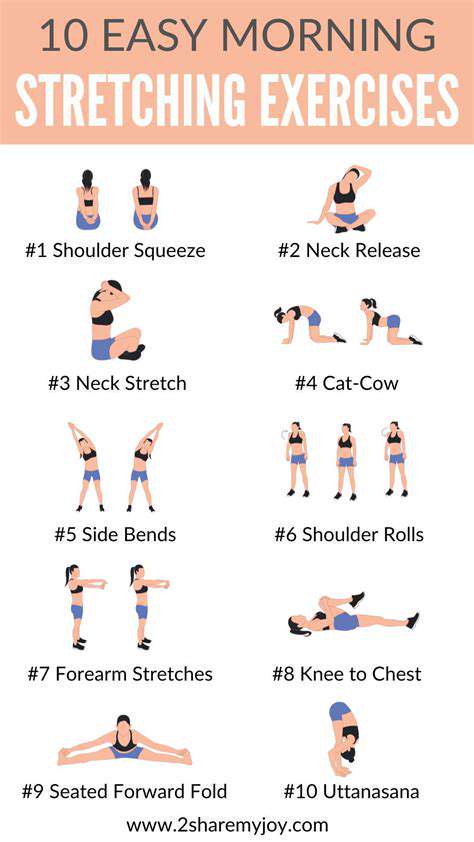
There are various types of balance exercises, ranging from simple standing exercises to more complex movements. Basic exercises might include single-leg stance, heel-to-toe walking, and standing on a cushion or unstable surface. These activities can be performed at home with minimal equipment.
More advanced exercises might include exercises on a balance board, using resistance bands for added challenge, or performing exercises while standing on one leg and doing a light arm movement.
Progressive exercises are critical to improving balance over time. Starting with simple exercises and gradually increasing the difficulty is key to building strength and improving stability.
Practical Application and Implementation
Incorporating balance exercises into your daily routine doesn't require a significant time commitment. Even 10-15 minutes of dedicated balance training, a few times a week, can yield noticeable improvements. Finding a quiet space at home or utilizing a gym, if accessible, is helpful.
Consider integrating balance exercises into your existing routine. For example, incorporate single-leg stance while brushing your teeth or waiting in line. These small, consistent efforts can significantly contribute to your overall balance improvement over time. Remember to listen to your body and modify exercises as needed to ensure safety and comfort.
Safety Precautions and Considerations
It's essential to prioritize safety when performing balance exercises. Beginners should start with simpler exercises and gradually increase the difficulty. Always ensure a stable and supportive surface when performing balance exercises. Using support, such as a chair or wall, is important to prevent falls.
Proper form is crucial for effective and safe exercise. Consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist for personalized guidance, especially if you have pre-existing medical conditions. They can help you create a safe and effective balance exercise program tailored to your specific needs and abilities. This personalized approach is critical for preventing injuries and ensuring optimal results.
The Role of Diet and Lifestyle in Maintaining Balance
Dietary Considerations for Maintaining Balance
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in supporting overall health and, consequently, balance. Nutrients like calcium and vitamin D are essential for strong bones, reducing the risk of fractures, which can significantly impact balance. Adequate protein intake is also important for maintaining muscle mass, which is vital for stability and preventing falls. Incorporating foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can help protect against oxidative stress, further contributing to overall well-being and balance.
Furthermore, hydration is paramount. Staying well-hydrated supports proper blood flow, nutrient transport, and overall bodily function, all of which contribute to maintaining balance and preventing dizziness. A diet rich in whole foods, lean proteins, and healthy fats is crucial for long-term balance and overall health in seniors.
Lifestyle Choices Affecting Balance
Maintaining an active lifestyle is paramount for maintaining balance and preventing falls. Regular physical activity, including exercises that improve strength, flexibility, and balance, is crucial. These exercises can include simple activities like walking, tai chi, or yoga, which can significantly improve balance and coordination. Consistency is key, aiming for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
The Importance of Regular Exercise
Regular exercise is crucial for maintaining muscle strength, flexibility, and balance. Exercises focusing on improving balance, such as standing on one leg or heel-toe walking, can significantly reduce the risk of falls. Incorporating strength training exercises, such as lifting weights or resistance bands, helps maintain muscle mass and power, which is essential for maintaining stability and balance. These exercises help improve proprioception, the body's awareness of its position in space, which is fundamental for balance.
Managing Underlying Health Conditions
Chronic health conditions, such as arthritis, diabetes, or vision problems, can significantly affect balance. Managing these conditions through regular medical check-ups, medication adherence, and lifestyle adjustments is crucial. Working closely with healthcare professionals to understand how these conditions may impact balance and developing strategies to mitigate those risks is essential for maintaining independence and safety.
The Impact of Sleep on Balance
Adequate sleep is vital for physical and cognitive function, including balance. When seniors don't get enough sleep, it can lead to decreased alertness, impaired coordination, and increased risk of falls. Prioritizing a regular sleep schedule, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and ensuring a conducive sleep environment can significantly improve sleep quality and, consequently, balance.
Environmental Factors and Fall Prevention
Evaluating and adapting the home environment to reduce fall risks is essential. Ensuring proper lighting, removing tripping hazards like loose rugs or cords, and installing grab bars in bathrooms and hallways can significantly reduce the likelihood of falls. Making these simple modifications can create a safer environment for maintaining balance and independence.
Stress Management and Balance
Chronic stress can negatively impact physical health and balance. Implementing stress-reducing techniques, such as meditation, yoga, or spending time in nature, can help improve overall well-being and reduce the risk of falls. Stress management plays a crucial role in maintaining balance, both physically and mentally, enabling seniors to maintain their independence and quality of life.