Functional Fitness for Seniors: Bending, Lifting, and Reaching Easier
Why Functional Fitness Matters for Seniors
Improving Balance and Stability
Maintaining balance and stability is crucial for preventing falls in seniors. Functional fitness exercises, tailored to individual needs, can significantly improve proprioception (the body's awareness of its position in space). These exercises often involve movements like standing on one leg, heel-to-toe walking, and performing squats or lunges with a controlled tempo. Practicing these activities regularly strengthens the muscles that support the joints, helping to maintain equilibrium and reducing the risk of debilitating falls. Improving balance is a key component of overall functional fitness, promoting independence and safety in daily activities.
Exercises that challenge balance, such as standing on an unstable surface or using a balance board, can be particularly effective. These activities engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, improving not only balance but also core strength and coordination. By incorporating these types of exercises into a regular routine, seniors can enhance their ability to navigate their environment safely and confidently, minimizing the risk of falls and maintaining an active lifestyle.
Enhancing Everyday Activities
Functional fitness isn't just about physical prowess; it's about enabling seniors to perform everyday tasks with ease and confidence. Exercises like reaching, bending, and lifting are vital for activities like getting dressed, reaching for items on shelves, or carrying groceries. Practicing these movements in a controlled and progressive manner strengthens the muscles required for these common actions, fostering greater independence and reducing reliance on assistance. By improving functional fitness, seniors can maintain their quality of life and continue engaging in their preferred activities.
Activities like gardening, light housework, and even playing with grandchildren often require bending, lifting, and reaching. Functional fitness training prepares seniors for these types of movements, ensuring they can participate in these activities with greater ease and less strain on their bodies. This proactive approach to fitness empowers seniors to continue living fulfilling lives, without limitations.
Boosting Cardiovascular Health
Functional fitness exercises often incorporate cardiovascular elements, such as brisk walking, stair climbing, or water aerobics. These activities not only improve cardiovascular health but also enhance overall stamina and endurance. A stronger cardiovascular system allows seniors to perform daily tasks with more energy and less fatigue. Increased blood flow delivers essential nutrients to muscles and organs, contributing to improved overall health and well-being. This sustained energy level helps seniors maintain an active lifestyle and engage in a wider range of activities.
Cardiovascular health is interconnected with functional fitness. Improved cardiovascular function directly supports the body's ability to perform various everyday movements. This seamless integration of cardiovascular and functional fitness exercises contributes significantly to overall health and vitality, empowering seniors to experience a higher quality of life.
Strengthening Muscles and Bones
Functional fitness exercises play a vital role in strengthening muscles and bones. Exercises that involve lifting, pushing, and pulling, mimicking activities of daily living, are particularly effective. These exercises not only build strength but also improve bone density, reducing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. Strengthening muscles and bones is crucial for maintaining independence and preventing age-related declines in mobility and functionality. By incorporating these exercises into a regular routine, seniors can significantly improve their ability to navigate their environment and participate in their desired activities.
Resistance training, an integral part of functional fitness, targets specific muscle groups to improve strength and endurance. These exercises also stimulate bone growth and repair, contributing to overall skeletal health and reducing the risk of falls and injuries. The combination of strength and balance exercises within a functional fitness program creates a comprehensive approach to maintaining mobility and independence in later life.
Mastering the Art of Bending
Understanding the Importance of Bending
Bending is a fundamental movement in daily life, from picking up groceries to reaching for items on shelves. For seniors, maintaining the ability to bend safely and effectively is crucial for preserving independence and quality of life. Proper bending techniques can prevent injuries and support overall physical well-being. This section will delve into the reasons why bending is so important, exploring how it affects activities of daily living (ADLs) and highlighting the risks of neglecting proper bending form.
Ignoring the art of bending can lead to a cascade of issues, ranging from minor inconveniences to more serious injuries. Poor form can strain muscles, ligaments, and joints, increasing the risk of falls and discomfort. The consequences can be far-reaching, impacting mobility and overall independence. Understanding the importance of bending ensures that seniors can navigate their daily routines with confidence and ease.
Safe Bending Techniques
Proper bending technique involves using your legs, not your back, to generate the power for bending. Keep your back straight and avoid twisting. Consider using a stool or chair to assist when reaching for objects that are out of your comfortable reach. This helps prevent strain on the spine and reduces the risk of injury.
Using your leg muscles to facilitate the bending motion is a key component of safe bending. This technique reduces the stress on your back, minimizing the possibility of back pain and injury. Ensuring proper posture during bending is equally important, as it helps maintain balance and reduces the risk of falls.
Strengthening Muscles for Bending
Building strength in the legs, core, and back muscles is essential for safe and effective bending. Exercises like squats, lunges, and planks can help strengthen these muscles. Regular exercise can improve balance and stability, further reducing the risk of falls during bending and other activities.
Strengthening exercises are crucial for maintaining the ability to bend safely and effectively. By focusing on core strength and leg strength, seniors can build the muscle support needed for daily tasks. This proactive approach to building strength minimizes the risk of injury and supports long-term physical health.
Bending and Lifting Techniques for Seniors
Bending and lifting should always be done with caution and proper technique. Lift with your legs, keeping your back straight, and avoid twisting. Consider using assistive devices like grab bars or lifting aids to make tasks easier and safer.
Common Bending Injuries and Prevention
Common injuries associated with improper bending include back pain, muscle strains, and sprains. By following safe bending techniques, seniors can significantly reduce their risk of these injuries. Regular stretching and maintaining good posture are also important preventative measures.
Understanding the potential for injury is an important step in preventing it. Recognizing the risks associated with improper bending allows seniors to take proactive steps to protect themselves from potential pain and discomfort. Preventing these injuries through conscious effort is crucial for maintaining independence.
Assessing Individual Needs and Limitations
Each senior's needs and limitations are unique. A healthcare professional or physical therapist can assess individual needs and provide personalized recommendations for safe bending and lifting techniques. This personalized approach ensures that exercises and techniques are tailored to the specific needs of the individual.
Adapting to individual needs is crucial for effective and safe bending. By acknowledging the unique requirements of each senior, healthcare professionals can develop personalized strategies that maximize safety and effectiveness. This targeted approach ensures that bending remains a manageable and achievable part of daily life, promoting independence and a high quality of life.
Tools and Aids for Enhanced Bending
Various tools and aids can assist seniors in safely bending and lifting. Examples include grab bars, long-handled reachers, and adaptive utensils. These tools can make daily tasks easier and reduce the risk of injury. Exploring and utilizing these aids can significantly enhance safety and independence.
Utilizing these tools can make a significant difference in the safety and ease of daily tasks. From simple grab bars in the bathroom to long-reach tools for grabbing items from shelves, these tools provide support and assistance, enabling seniors to maintain their independence and participate fully in life.
Efficient Lifting Techniques for Seniors
Proper Form for Bending Exercises
Maintaining proper form during bending exercises is crucial for seniors to avoid injuries and maximize effectiveness. Focus on engaging your core muscles throughout the movement. This core engagement helps stabilize the spine and reduces strain on the lower back. Imagine drawing your belly button towards your spine, keeping your back straight and your chest lifted. This controlled movement prevents unnecessary stress on joints and promotes a safe and effective workout.
A good rule of thumb is to bend from the hips, keeping your knees slightly bent. Avoid rounding your back or slouching as you bend. This will help to protect your spine and prevent potential injuries. Practice in front of a mirror to ensure your posture is correct and to identify any areas needing improvement. A qualified physical therapist or certified personal trainer can provide personalized guidance.
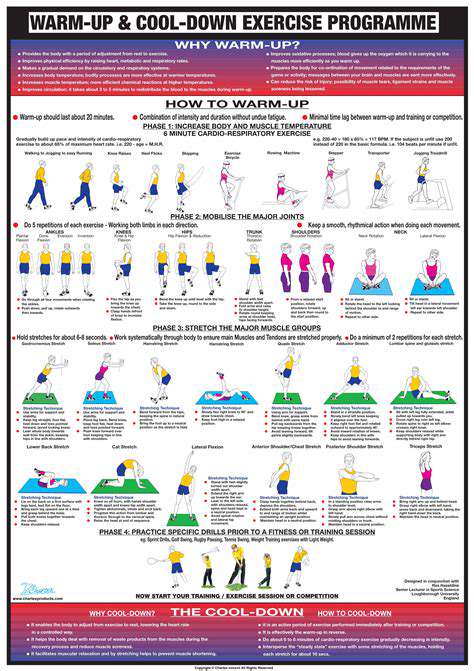
Importance of Warm-up and Cool-down
Before engaging in any bending exercises, a proper warm-up is essential to prepare your muscles and joints for the activity. Gentle stretching, such as arm circles, leg swings, and torso twists, can help increase blood flow and flexibility. This warm-up period prepares your body for the demands of the exercises. A consistent warm-up routine reduces the risk of muscle strains and improves overall performance.
Similarly, a cool-down period after bending exercises is just as important. Gentle stretching of the muscles used in the exercises can help to restore flexibility and prevent stiffness. Holding each stretch for 15-30 seconds allows the muscles to recover and promotes a smoother transition back to everyday activities. This post-exercise routine promotes recovery and reduces the risk of delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS).
Choosing Appropriate Weights and Resistance
When incorporating weights or resistance bands into bending exercises, it's vital to start with a manageable weight or resistance level. Beginners should choose light weights or minimal resistance, gradually increasing the intensity as strength and endurance improve. Overexertion can lead to injuries, so it's crucial to prioritize proper form over lifting heavy weights. Listening to your body is key; if you experience pain, stop the exercise and rest.
Using resistance bands, start with a band with low resistance and work your way up to a higher resistance band as you get stronger. The important thing is to choose a weight or resistance that allows you to maintain proper form throughout the exercise. This approach promotes safe and effective progress without jeopardizing your well-being.
Modifications for Specific Needs
Seniors with specific physical limitations or conditions may require modifications to bending exercises. For instance, individuals with arthritis might benefit from using lighter weights or resistance bands, or modifying the range of motion. Consider using chairs or benches for support during exercises to reduce strain on joints. Consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist for personalized recommendations and modifications based on individual needs.
Adjusting exercises to accommodate specific needs and limitations is crucial for safe participation and effective results. This individualized approach allows seniors to participate actively in their fitness journey while minimizing risks. A qualified professional can provide guidance and support in adapting exercises to meet specific physical challenges.
Safety Precautions During Bending Exercises
Safety should always be the top priority during bending exercises for seniors. Pay close attention to your body's signals, and stop if you experience any pain or discomfort. Avoid forcing yourself into positions that feel uncomfortable or strenuous. Ensure a stable and secure environment to prevent falls or accidents. Having a sturdy chair or wall nearby can provide support and balance.
Proper supervision during exercise, especially for seniors new to these types of exercises, is crucial. This can reduce risk of injury and ensure a positive experience. Consulting with a healthcare professional or certified personal trainer before starting any new exercise program is recommended to ensure it aligns with individual health conditions and abilities. Focusing on good form and listening to your body are paramount to a safe and effective exercise routine.
Reaching for the Stars (Safely!)

Preparing for Your Journey
Before embarking on any space exploration, meticulous planning is paramount. This involves not only assessing the destination's potential hazards but also carefully considering the resources necessary for a safe and successful mission. Understanding the specific challenges posed by the target environment, such as extreme temperatures or radiation levels, is critical for equipping the spacecraft and crew adequately. A comprehensive risk assessment, encompassing potential malfunctions and unforeseen circumstances, is essential to mitigate potential dangers.
Thorough training for the crew is vital, ensuring that they possess the necessary skills and knowledge to handle unexpected situations. This includes extensive preparation for emergency procedures, spacecraft operation, and the psychological impact of prolonged space travel. Preparing for the isolation and confinement of space travel is just as important as mastering technical skills.
Navigating the Vastness of Space
Successfully navigating the vast expanse of space requires precise calculations and advanced technologies. Precise trajectory planning is essential to reach the desired destination efficiently and safely, accounting for gravitational influences from celestial bodies. This intricate process demands sophisticated algorithms and powerful computing systems to predict and adjust for any deviations encountered during the voyage.
Modern spacecraft rely on complex guidance systems, utilizing a combination of onboard sensors and communication with ground control. These systems allow for real-time adjustments to course corrections, maintaining the spacecraft's trajectory on its intended path. Real-time adjustments and constant monitoring are critical to the mission's success.
Overcoming the Challenges of Deep Space
The further humanity ventures into space, the more significant the challenges become. Deep space travel presents unique problems, including the long duration of journeys and the potential for equipment malfunctions. Maintaining the health and well-being of the crew for extended periods is crucial, demanding specialized provisions for sustenance, hygiene, and medical care.
The isolation and confinement of space travel can have a profound impact on human psychology. Careful consideration must be given to the psychological needs of the crew, including opportunities for recreation, communication with loved ones, and stress management techniques. These factors are essential for maintaining morale and preventing potential psychological issues during long-duration missions.
Ensuring a Safe Return
Returning from a space mission is just as challenging as the journey itself. Careful planning is crucial to ensure a safe return, taking into account the specific conditions encountered during the mission and any potential damage to the spacecraft or changes in its trajectory. The return trajectory must be meticulously calculated, factoring in the precise gravitational forces and potential obstacles.
Re-entry into Earth's atmosphere presents a significant hazard. The intense heat and pressure generated during this process require specialized heat shields and robust designs to protect the spacecraft and its occupants. Careful monitoring of atmospheric conditions and spacecraft performance is essential for a safe return.