Safe Lifting Techniques for Seniors with Osteoporosis
Assessing Your Osteoporosis and Lifting Capacity

Understanding Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a bone disease that develops when the body loses excessive bone mass or produces insufficient new bone tissue. This condition results in fragile bones that fracture easily, particularly in vulnerable areas like the hips, spine, and wrists. Recognizing osteoporosis risks proves essential for both prevention and timely treatment. Contrary to common belief, this condition doesn't exclusively affect older adults - people of all ages should take preventive measures.
Risk Factors for Osteoporosis
Multiple elements contribute to osteoporosis development. Aging naturally reduces bone density, but other factors play equally important roles. Genetic predisposition significantly influences risk levels, especially when family members have experienced osteoporosis. Medical conditions including rheumatoid arthritis and celiac disease may accelerate bone loss. Lifestyle choices such as tobacco use, heavy alcohol consumption, and insufficient weight-bearing exercise all negatively impact bone health.
Assessing Bone Density
Bone density evaluation forms the cornerstone of osteoporosis risk assessment. Specialized tests like DEXA scans measure bone mineral content with precision. These scans compare individual results against age and gender-matched averages. DEXA findings help identify current osteoporosis cases or predict future risk, providing critical data for developing personalized treatment strategies.
Lifestyle Modifications
Adopting bone-friendly habits can dramatically lower osteoporosis risk. A nutrient-rich diet containing adequate calcium and vitamin D supports skeletal strength. Weight-bearing physical activities like walking, jogging, and dancing stimulate bone remodeling and strengthening. Eliminating smoking and moderating alcohol intake further protect bone integrity.
Dietary Considerations for Bone Health
Optimal bone health requires sufficient calcium and vitamin D intake. Calcium serves as the primary building block for bone tissue, while vitamin D enhances calcium absorption. Excellent calcium sources include dairy products, dark leafy greens, and fortified foods. When dietary intake falls short, targeted supplementation becomes necessary for comprehensive bone protection.
Medical Interventions for Osteoporosis
When lifestyle changes prove insufficient, medical treatment may become necessary. Various medications can improve bone density and reduce fracture likelihood. Consulting healthcare professionals ensures personalized treatment plans based on individual bone scans and specific health circumstances.
Importance of Early Detection and Treatment
Timely osteoporosis diagnosis and intervention prevent debilitating fractures and preserve quality of life. Early treatment slows bone loss progression and substantially decreases fracture risks. Regular medical evaluations facilitate early problem detection, enabling prompt protective measures that yield better long-term outcomes.
Choosing the Right Lifting Posture
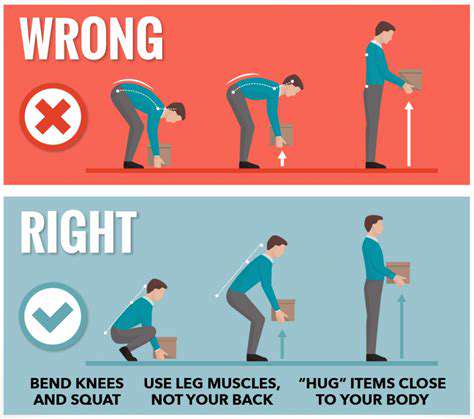
Proper Lifting Techniques for Safety
Correct lifting form prevents injuries, particularly back problems. Proper technique reduces spinal stress and muscle strain, minimizing risks of sprains, strains, and disc injuries. Effective lifting involves core muscle engagement for spinal stability and keeping loads close to the body. These methods don't just prevent immediate pain - they safeguard long-term musculoskeletal health.
Mastering proper lifting techniques represents an investment in lifelong physical well-being. Activating core muscles while maintaining close contact with loads dramatically decreases spinal pressure and tissue stress.
Assessing the Load and Your Capabilities
Before lifting, thoroughly evaluate the object's weight and dimensions relative to your physical capacity. Consider potential obstacles and whether assistance might be necessary. Understanding both personal limits and load characteristics ensures safe lifting practices.
For heavy or awkward items, never lift alone. Request help or use mechanical aids to prioritize safety above all else.
Maintaining a Neutral Spine
Keeping the spine neutral during lifts prevents excessive strain. Visualize maintaining a straight alignment from skull to pelvis. This position optimizes back muscle efficiency while minimizing spinal stress.
Using Your Legs, Not Your Back
Power lifts should originate from leg muscles, not the back. Engaging quadriceps and hamstrings provides necessary strength and stability, distributing load forces throughout the body. This technique represents the safest lifting method for injury prevention.
Approach lifting like performing squats - bending knees and hips while keeping the back straight maximizes leverage and control.
Choosing the Right Lifting Equipment
Appropriate lifting aids like hand trucks, dollies, or straps significantly reduce physical strain. These tools redistribute weight forces, decreasing back pressure. Quality lifting equipment forms a critical workplace safety component that protects long-term health.
Select equipment based on object characteristics - size, shape, and weight all influence the optimal choice. Careful selection ensures both safety and efficiency.
Important Considerations for Everyday Lifting
Proper Posture and Body Mechanics
Optimal posture and biomechanics prove especially important for senior lifting safety. Maintain spinal alignment while avoiding waist bending or twisting. Generate lifting power from leg muscles by bending knees and hips, which evenly distributes weight and reduces spinal stress. Core muscle engagement provides additional torso stability during lifting and placement maneuvers.
Establish a wide, stable base by positioning feet shoulder-width apart or slightly wider. This enhances balance and prevents slips. For high objects, use proper supports to avoid dangerous reaching.
Lifting Objects of Varying Weights and Sizes
Adapting techniques to different loads prevents injuries. Heavy objects require careful planning and gradual lifting. Evaluate weight and size beforehand, seeking assistance when needed. Breaking lifts into smaller steps improves control and reduces strain.
Identify the object's center of gravity for balanced lifting. For irregular items, utilize appropriate tools like carts or dollies to minimize physical stress.
Assessing Your Physical Limitations and Seeking Assistance
Honest self-assessment prevents overexertion injuries. Seniors should acknowledge strength and flexibility changes that may complicate lifting tasks. Don't hesitate to request help when needed - prevention outweighs potential injury consequences. Listen to your body's warning signals for optimal safety.
Discontinue lifting immediately if pain occurs, consulting healthcare professionals for evaluation and recovery guidance.
Preventing Falls and Injuries
Identifying Potential Fall Hazards
Fall prevention becomes crucial for osteoporosis patients due to increased fracture risks. Conduct thorough home safety assessments, addressing poor lighting, clutter, loose rugs, and uneven surfaces. These modifications significantly reduce fall risks while maintaining independence.
Regularly inspect all living spaces for tripping hazards like loose cords or floor objects. Implement solutions like rug securing and bathroom grab bars. Remember to evaluate both indoor and outdoor areas.
Proper Footwear Selection
Appropriate shoes dramatically impact fall prevention. Osteoporosis patients need footwear with excellent support and traction. Avoid slippery soles or high heels that increase fall risks. Choose shoes with sturdy, textured outsoles for superior grip across surfaces.
Match footwear to specific activities - outdoor walking shoes differ from indoor options. Proper fit ensures optimal support and comfort.
Utilizing Assistive Devices
Canes and walkers enhance stability for osteoporosis patients. Properly fitted devices provide essential support, particularly for those with balance challenges. Consult healthcare professionals to identify the most suitable assistive equipment.
Maintaining Good Posture and Balance
Proper posture and balance exercises help prevent falls. Targeted workouts strengthen core muscles and improve stability, reducing everyday fall risks.
Safe Lifting Techniques
Proper lifting methods prevent falls and injuries. Use leg strength, maintain straight backs, and avoid twisting motions. Keep objects close to your body, using assistive devices or help for challenging items.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Regular consultations with physical therapists and physicians provide personalized osteoporosis management strategies. These experts recommend customized prevention techniques, assistive devices, and safe exercises for optimal bone health maintenance.