Simple Strength Exercises for Seniors Over 80
Gentle Strength Training for Seniors

Benefits of Gentle Strength Training
Many older adults discover that gentle strength training provides numerous advantages that extend well beyond maintaining muscle tone. Enhancing balance and coordination plays a vital role in reducing fall risks, which remain a primary concern for injury among the elderly population. Through consistent strength training, individuals can improve these critical skills, leading to greater safety and self-reliance in daily activities. Additionally, such exercises contribute to better bone density, helping to prevent osteoporosis and lower fracture risks.
Maintaining independence in daily life represents another significant benefit. By strengthening the muscles used for common movements like standing from a seated position, reaching overhead, or carrying packages, seniors can perform these tasks more comfortably. This increased capability directly enhances quality of life, enabling continued participation in social and community activities.
Selecting Suitable Exercises
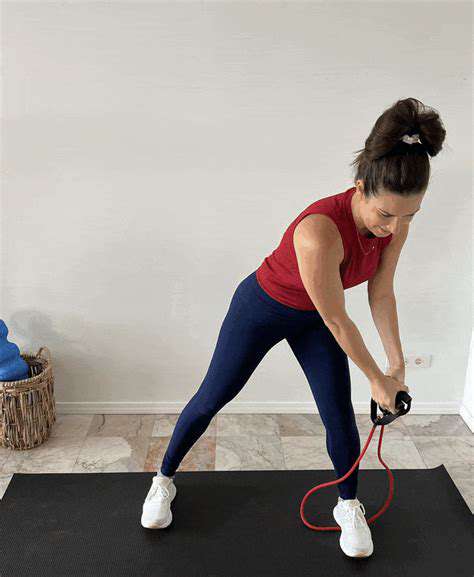
Choosing appropriate movements forms the foundation of any safe and productive strength training regimen. Focus on activities that engage major muscle groups including the lower body, upper extremities, and core muscles. Emphasize smooth, controlled motions rather than quick, jerky movements to minimize injury potential, particularly important for those with existing health concerns.
Resistance bands, light hand weights, or bodyweight exercises serve as excellent starting options. These methods allow for gradual strength development without excessive joint strain. Always remain attentive to your body's signals and adjust exercises as necessary for comfort and safety. Consulting with a medical professional or certified trainer can help create a customized program addressing individual needs and limitations.
Essential Safety Measures
Prioritizing safety remains critical when beginning any exercise program, especially for mature adults. Begin each session with proper warm-up activities, slowly increasing intensity to prepare muscles and joints. Concluding with appropriate cool-down exercises proves equally important, helping the body transition back to a resting state. Maintaining correct posture and technique throughout each movement reduces injury risk while ensuring proper muscle engagement.
Never ignore pain or significant discomfort during exercise. Should pain occur, immediately discontinue the activity and consult a healthcare provider. Proper hydration before, during, and after workouts also remains essential. Using suitable equipment and exercising in a safe environment represent additional important considerations for injury prevention.
Progressing Safely
Regular participation represents the most important factor for achieving results from any exercise program. Aim for consistent workouts several times weekly to gradually build strength and endurance. Slowly increase resistance levels or repetition counts as your capabilities improve. This methodical approach stimulates continued muscle development while minimizing injury risk. Remember that noticeable changes take time, so patience and persistence prove essential.
Documenting your workout progress can provide valuable motivation. Keep records of exercises performed and improvements noticed. This tangible evidence of progress helps maintain enthusiasm and commitment to your fitness objectives. Celebrate all achievements, regardless of size, to sustain a positive mindset toward your health goals.

Flexibility and Stretching Exercises
Why Flexibility Matters
Maintaining flexibility becomes increasingly important as we age, significantly influencing overall health and daily functioning. Reduced flexibility often leads to stiffness, discomfort, and limited mobility, making routine activities like dressing or reaching more difficult. Regular stretching can dramatically improve joint range, decrease discomfort, and enhance stability, all contributing to greater independence. The benefits become apparent quickly, demonstrating that starting a stretching routine at any age proves beneficial.
Flexibility exercises also promote better posture and reduced fall risk. Proper alignment helps maintain balance and prevents injuries. Stretching strengthens the muscles supporting the spine, improving posture and making falls less likely. Making these exercises part of your daily routine represents an investment in long-term health and self-sufficiency.
Safe Stretching Methods
When initiating a stretching routine, always emphasize gentle movements and avoid overexertion, particularly with existing health conditions. Hold each stretch for 15-30 seconds, gradually extending duration as flexibility increases. Pay close attention to your body's signals and stop immediately if sharp pain occurs. Proper breathing technique also plays a crucial role - inhale deeply when moving into the stretch and exhale while holding the position.
Simple movements like slow arm circles, gentle leg swings, and controlled torso rotations can significantly enhance flexibility. These can be performed either seated or standing, accommodating various mobility levels. Focus on smooth, controlled motions rather than bouncing movements. For best results, aim for 15-20 minutes of stretching most days each week.
Recommended Exercises
Tailoring stretches to meet the specific needs of older adults ensures maximum benefit with minimal risk. Gentle hamstring stretches performed while lying down can improve lower body flexibility. Similarly, quadriceps stretches help maintain thigh muscle elasticity. These exercises can be modified for those with limited mobility by performing them while seated.
Neck rotations and shoulder stretches also prove beneficial, helping maintain upper body mobility and reduce stiffness. These simple movements can easily become part of a daily routine regardless of physical limitations.
Preparation and Recovery
Proper warm-up before stretching remains essential to prevent injury and maximize benefits. Begin with 5-10 minutes of light activity like walking or chair exercises to increase blood flow. Similarly, concluding with a cool-down period allows the body to gradually return to its resting state, reducing muscle soreness and promoting recovery.
Proper Technique and Safety Guidelines
Mastering Correct Form
Proper technique during strength exercises remains paramount for achieving optimal results while minimizing injury risk, particularly for older adults. Correct form ensures targeted muscles work efficiently without placing undue stress on joints and surrounding tissues. This becomes especially important for seniors, as proper technique helps preserve joint health and stability - critical factors in fall prevention and maintaining independence.
Learning proper form involves understanding each exercise's specific mechanics. Instructional videos or professional demonstrations can prove extremely helpful. Consulting with a certified trainer or physical therapist provides personalized guidance, particularly valuable for beginners or those with health concerns.
Essential Safety Tips
Prior medical consultation remains crucial before starting any new exercise program, ensuring activities align with individual health status and capabilities. This helps identify any potential limitations or health considerations affecting safe participation.
Proper warm-up and cool-down periods prove equally important. Begin with 5-10 minutes of light activity and gentle stretching to prepare the body, and conclude with similar activities to promote recovery and reduce muscle soreness.
Selecting Appropriate Resistance
Choosing suitable resistance levels remains critical for both progress and safety. Begin with lighter resistance and gradually increase as strength improves. Always listen to your body - if pain occurs, stop immediately and consult a healthcare professional.
The ideal resistance allows completion of desired repetitions while maintaining proper form. Excessive weight compromises technique and increases injury risk, while insufficient resistance limits progress.
Effective Breathing Techniques
Proper breathing significantly enhances exercise performance and safety. Inhale during less strenuous phases and exhale during more challenging portions. This breathing pattern helps maintain stability and control while improving exertion tolerance.
Gradual Progression
Consistency forms the foundation of any successful exercise program. Establish a regular schedule of 2-3 weekly sessions with adequate rest between workouts. Gradually increasing resistance, repetitions, or sets as strength improves stimulates continued progress while minimizing injury risk.
Tracking and Adjustments
Regular progress monitoring allows for necessary adjustments. Note how your body responds to exercises and modify accordingly if discomfort occurs. Professional guidance can help make informed decisions about program modifications as fitness levels change.
Recovery Importance
Adequate rest between workouts proves essential, particularly for older adults. Allowing muscles time to repair promotes optimal results and prevents overuse injuries. Sufficient sleep, proper nutrition, and light activity on rest days all contribute to effective recovery and overall wellbeing.