The Physical Benefits of Gardening for Seniors
Improved Physical Fitness and Mobility
Improved Cardiovascular Health
Gardening activities, such as digging, weeding, and carrying tools, can significantly elevate your heart rate and improve cardiovascular health. Regular engagement in these physical tasks helps strengthen the heart muscle, improving its efficiency in pumping blood throughout the body. This increased cardiovascular fitness can lead to lower blood pressure and a reduced risk of heart disease, a critical concern for seniors. The rhythmic motions involved in gardening also contribute to overall circulation and oxygen delivery, benefiting various bodily functions.
Furthermore, the consistent exertion involved in gardening can help maintain a healthy weight, a factor closely linked to cardiovascular health. A calorie-burning activity like gardening can be incorporated into a senior's daily routine, contributing to weight management and reducing the risk of obesity-related health issues, which are common in older adults.
Enhanced Muscle Strength and Endurance
Gardening tasks, like lifting and carrying soil, plants, and tools, provide a natural resistance training, strengthening muscles in the arms, legs, and back. Regular gardening can help combat muscle atrophy, a common issue in aging, which leads to decreased strength and mobility. The varied movements involved in gardening engage different muscle groups, promoting overall strength and endurance.
The repetitive motions inherent in many gardening tasks, such as digging, planting, and pruning, also help build endurance. This continuous physical activity strengthens muscles and improves the body's ability to sustain physical exertion over time. Improved endurance can significantly impact a senior's daily activities, making tasks like walking, climbing stairs, and performing household chores easier and more manageable.
Increased Bone Density
Weight-bearing exercises, which are integral to gardening, stimulate bone growth and density. Activities like digging, lifting, and carrying contribute to bone strengthening, effectively combating age-related bone loss and osteoporosis, a prevalent concern among seniors. This enhanced bone density is crucial for maintaining balance, preventing falls, and supporting overall skeletal health.
Improved Balance and Coordination
The varied movements involved in gardening, including bending, reaching, and twisting, contribute to enhanced balance and coordination. These exercises are often overlooked, but they are essential for maintaining stability and preventing falls, which are a significant concern for seniors. The continuous engagement with the garden environment also improves spatial awareness and proprioception, which are essential for maintaining balance and coordination.
The act of navigating garden pathways, maneuvering around plants, and handling tools all contribute to improving a senior's balance and coordination. This active engagement with the environment and the tasks at hand promotes a more confident and secure movement pattern, reducing the risk of falls and improving overall mobility.
Flexibility and Range of Motion
Gardening often involves reaching, bending, twisting, and stretching, all of which contribute to increased flexibility and range of motion. These movements help maintain the elasticity and suppleness of muscles and joints, reducing stiffness and improving overall mobility. Regularly engaging in these motions can help seniors maintain their flexibility, making daily activities more comfortable and less strenuous.
The repeated stretching and bending involved in gardening exercises, such as planting, pruning, and weeding, directly improve the range of motion in the joints. This improved flexibility reduces the risk of joint pain and stiffness, which are often associated with aging and can significantly impact a senior's mobility and quality of life.
Reduced Stress and Improved Mental Well-being
Engaging in gardening activities provides a healthy outlet for stress relief and promotes a sense of accomplishment. Spending time outdoors in nature, surrounded by plants and the elements, has a calming effect, decreasing stress hormones and promoting relaxation. This, in turn, improves mental well-being and overall emotional health, which are crucial for seniors' overall quality of life.
The act of nurturing plants, observing their growth, and taking care of the garden can be incredibly therapeutic. The sense of accomplishment derived from tending to a garden can boost self-esteem and improve mood. These positive emotional benefits can be a significant factor in maintaining a senior's mental well-being and promoting overall health and happiness.

Social Engagement and Community Building
Fostering Social Connections Through Gardening Activities
Participating in community gardening projects provides seniors with a valuable opportunity to connect with others who share similar interests. These activities encourage meaningful conversations and foster friendships, reducing feelings of loneliness and isolation. When seniors work together on planting, maintaining, and harvesting gardens, they develop a sense of camaraderie that enhances their emotional well-being.
Engaging in group gardening sessions also facilitates the exchange of knowledge and gardening tips among participants. This collaborative environment not only promotes social bonding but also empowers seniors to learn new skills and share their life experiences. As a result, community gardens serve as vital social hubs that strengthen interpersonal relationships among elderly individuals.
Building a Sense of Community and Purpose
Community gardening initiatives instill a sense of purpose in seniors by involving them in meaningful activities that contribute to the well-being of their neighborhood. When seniors see the tangible results of their efforts—such as blooming flowers or fresh vegetables—they experience a boost in self-esteem and pride. This sense of accomplishment encourages continued participation and fosters a feeling of belonging.
Moreover, these communal spaces often become focal points for local events, educational workshops, and cultural celebrations, further enhancing community cohesion. Seniors who actively participate in these events often report increased feelings of inclusion and a stronger connection to their community.
Encouraging Intergenerational Interaction
Gardening projects that include participants from different age groups create opportunities for intergenerational bonding. Grandparents, parents, and children working together in the garden learn from one another, sharing different perspectives and skills. These interactions promote mutual understanding and respect, enriching the social fabric of the community.
In addition, involving young people in gardening activities with seniors helps bridge the generation gap, fostering empathy and appreciation for the experiences of older adults. Such programs often lead to lasting relationships that benefit both age groups and contribute to a more inclusive community environment.
Enhancing Mental Health Through Social Engagement
Engaging with others in a gardening setting can significantly improve mental health by reducing symptoms of depression and anxiety among seniors. The social interactions and shared goals help combat feelings of loneliness and provide emotional support. Being part of a community creates a sense of security and belonging that is vital for mental well-being.
Research indicates that seniors involved in community gardening report higher levels of happiness and lower stress levels. The social component of gardening acts as a natural antidepressant, promoting positive emotions through meaningful connections and shared accomplishments.
Supporting Physical Activity and Mobility in Social Contexts
Social gardening activities often involve light physical exercises such as planting, watering, and weeding, which are beneficial for maintaining mobility and strength. When these activities are performed in groups, they encourage seniors to stay active regularly, leveraging social motivation to adhere to physical activity routines.
This social aspect also provides opportunities for seniors to assist and motivate each other, creating an encouraging environment that promotes sustained physical engagement. As a result, community gardening can be an effective way to combine physical health benefits with social interaction, making exercise more enjoyable and less isolating.
Creating Support Networks and Volunteer Opportunities
Community gardens often serve as platforms for seniors to volunteer and support one another, fostering a culture of mutual aid. Volunteering in garden maintenance or educational programs helps seniors feel valued and purposeful, boosting their self-worth and social integration.
These support networks can extend beyond the garden, providing seniors with resources and assistance for other aspects of life, such as healthcare or transportation. The sense of being part of a caring community enhances overall life satisfaction and resilience among elderly participants.
Promoting Inclusivity and Accessibility in Community Spaces
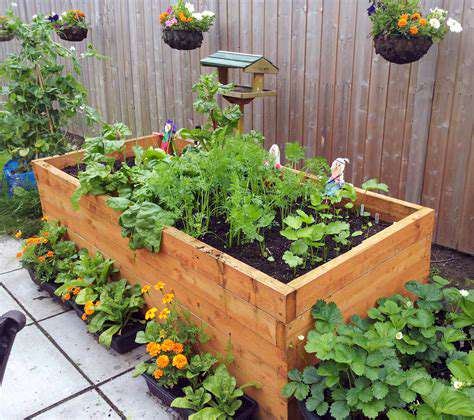
To maximize social engagement, community gardens should prioritize inclusivity by designing accessible features that accommodate seniors with mobility challenges. Raised beds, paved pathways, and ergonomic tools enable older adults to participate comfortably and independently.
Creating welcoming environments encourages diverse participation, ensuring that all seniors, regardless of physical ability, can enjoy the social and physical benefits of gardening. Such inclusive spaces foster a sense of equality and community pride, strengthening social bonds across different groups.