8 Functional Exercises to Improve Senior Independence
Understanding the Importance of Independence
Preserving autonomy as we age isn't just about physical capability - it's about sustaining the dignity of self-sufficiency. The capacity to manage daily routines, make personal choices, and participate in meaningful activities forms the bedrock of psychological well-being. When these abilities diminish, the emotional toll can be profound, often leading to withdrawal from social connections and diminished life satisfaction.
What many don't realize is that independence isn't an all-or-nothing proposition. Through targeted strategies and adaptive approaches, older adults can maintain significant control over their lives even as certain physical capabilities change. This nuanced understanding helps families provide support without undermining self-determination.
The Role of Functional Fitness
Movement quality matters more than muscle size when it comes to daily living. Functional fitness focuses on training the body for real-world situations - lifting grocery bags rather than barbells, navigating stairs instead of stairmasters. This practical approach bridges the gap between exercise and everyday needs.
Identifying Potential Challenges
The aging process brings predictable physical changes that can affect independence if unaddressed. Muscle fibers naturally decrease in number and size after age 30, with acceleration after 60. Joint cartilage wears down over decades of use. Reaction times slow. These aren't reasons for resignation but rather signposts for proactive intervention.
Vision changes, medication side effects, and home environment hazards compound these biological factors. A comprehensive approach considers all these elements when creating an independence preservation plan.
The Benefits of Exercise
Physical activity serves as the closest thing we have to a fountain of youth. Beyond the obvious cardiovascular benefits, regular movement stimulates neurogenesis (brain cell growth), enhances proprioception (body awareness), and maintains the elasticity of connective tissues. The key lies in selecting activities that address multiple systems simultaneously - a tai chi session, for instance, improves balance, flexibility, and mental focus in one integrated practice.
Prioritizing Safety and Modifications
Exercise programming for older adults requires careful calibration. A movement that strengthens a 40-year-old might destabilize someone at 70. This isn't about limitation but about precision. Chair-based exercises, water workouts, and resistance bands often provide safer alternatives to traditional gym equipment.
The most effective trainers working with seniors don't just modify exercises - they reframe them as adaptive victories rather than concessions to age. This psychological shift makes all the difference in long-term adherence.
Choosing the Right Exercises
Effective programming starts with a movement audit - what specific actions does this individual need to perform independently? For someone who struggles getting out of their favorite armchair, seated-to-standing drills take priority. For grandparents who want to lift grandchildren safely, functional carrying exercises prove most relevant.
Consistency and Patience
The paradox of aging well is that the process can't be rushed but must be continual. Unlike youth fitness where dramatic transformations occur in weeks, mature bodies respond best to gradual, sustained effort. Small daily investments compound into significant functional capital over months and years.
Tracking non-scale victories - easier laundry days, steadier stair climbing - provides more meaningful motivation than conventional fitness metrics. These tangible improvements in life quality fuel ongoing commitment.
8 Key Functional Exercises for Seniors

Strength Training for Seniors
Muscle preservation becomes increasingly vital after 60, when sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss) accelerates. Unlike cosmetic bodybuilding, functional strength training prioritizes movements over muscles. A well-designed program might include sit-to-stands using varying chair heights to mimic real-world scenarios. These practical applications make the benefits immediately perceptible in daily life.
Resistance doesn't require fancy equipment - bodyweight exercises, water bottles, or even canned goods can provide effective training stimuli when used with proper technique and progression.
Improving Balance and Coordination
Balance work should progress from stable surfaces (holding a chair) to unstable ones (foam pads) as ability improves. The most effective routines incorporate dual-tasking - reciting the alphabet while balancing, for instance - to simulate real-world cognitive-motor challenges. This integrated approach builds fall-resistant neural pathways.
Flexibility and Range of Motion
Dynamic stretching (moving while stretching) often proves more functional for seniors than static holds. Arm circles that gradually increase in diameter prepare shoulders for reaching overhead cabinets better than prolonged stretches. The key is moving joints through their full available range regularly throughout the day.
Cardiovascular Health
Interval training adapted for seniors - alternating brisk walking with gentle strolling - provides cardiovascular benefits without joint stress. Non-impact options like recumbent cycling or aquatic exercises allow those with arthritis to maintain heart health. The best cardio is what can be done consistently with enjoyment.
Core Strength and Stability
Modified core work like seated marches or standing abdominal bracing protects the back while building essential stability. These adaptations allow even those with spinal issues to develop the core endurance needed for prolonged sitting or standing.
Exercises for Hand and Wrist Strength
Grip strength correlates with longevity, making hand exercises surprisingly vital. Simple tools like therapy putty or rubber bands provide progressive resistance for pinching, squeezing, and extending motions needed for utensils, keys, and medication bottles.
Proper Form and Safety Precautions
Mirror training helps seniors develop body awareness for proper alignment. Working with a professional initially to establish motor patterns prevents ingraining harmful movement habits. Quality always trumps quantity in mature fitness.
Orlando, famous for its heart-pounding theme park rides, also boasts an impressive array of cultural treasures many visitors overlook. The city's artistic offerings provide meaningful counterpoints to its thrill rides - where rollercoasters deliver adrenaline, museums nourish the soul. The Orlando Museum of Art's collection tells human stories across centuries, inviting reflection amid vacation excitement. These cultural touchstones create balanced family experiences that engage multiple dimensions of being.
Upper Body Strength and Mobility
Importance of Upper Body Strength
Arm strength directly enables personal care - from brushing hair to adjusting clothing. Shoulder mobility determines whether one can reach that top shelf or wash their own back. These aren't vanity metrics but essential independence indicators.
Improving Upper Body Mobility
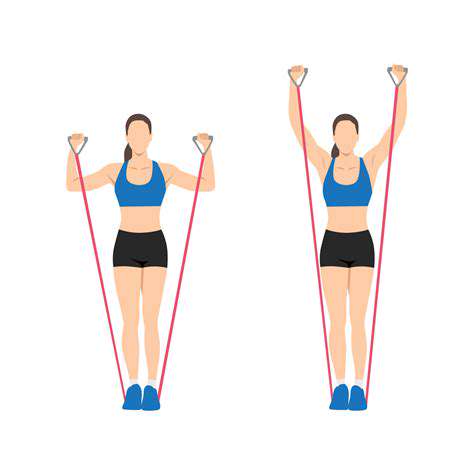
Wall slides, where hands glide up a surface while maintaining contact, safely restore overhead reach. Resistance band rows rebuild pulling strength for opening heavy doors or rising from chairs. The goal isn't bodybuilding but maintaining enough strength for life's physical demands.
Functional Exercises for Seniors
Carrying weighted bags of increasing load trains both grip and arm endurance for groceries. Pushing a wall mimics rising from surfaces or opening stuck windows. These contextualized movements build confidence along with capacity.
Exercises for Shoulder Stability
Rotator cuff exercises using minimal resistance prevent the shoulder injuries that commonly plague older adults. External rotations with light bands maintain joint integrity for reaching and lifting motions.
Exercises for Arm Strength and Endurance
Modified push-ups against counters or walls develop functional pushing strength. Bicep curls with light weights maintain arm tone for carrying grandchildren or laundry baskets.
Importance of Proper Form and Progression
Video analysis helps seniors see their form objectively. Starting with just 2-3 repetitions of perfect form builds safer foundations than rushing into higher volumes with compromised technique.
Core Stability and Flexibility

Core Stability: The Foundation
The deep core muscles act as nature's back brace, stabilizing the spine during all movement. Unlike showy six-pack muscles, these deeper layers work continuously at low intensity. Training them involves subtle engagement rather than dramatic motion.
The Importance of Flexibility
Flexibility preserves freedom of movement - the ability to turn and see behind while driving, or bend to tie shoes. Dynamic stretches that move joints through their ranges maintain this crucial mobility better than static stretching for many seniors.
Core Stability and Flexibility Synergy
A stable core enables safer stretching by protecting the spine. Conversely, flexible muscles allow proper core engagement by preventing compensatory tightness. This interdependence explains why comprehensive programs address both.
Exercises for Core Stability
Breathing drills that focus on expanding the ribcage sideways activate often-neglected core stabilizers. Seated balance challenges on stability cushions build core responsiveness in safe positions.
Exercises for Flexibility
Gentle yoga flows link breath with movement to improve flexibility holistically. Foam rolling before stretching enhances tissue pliability for greater range of motion gains.
The Role of Posture in Core Stability and Flexibility
Posture check-ins throughout the day reinforce core engagement. Simple cues like ear over shoulder over hip help maintain alignment during daily activities.
Injury Prevention through Core Stability and Flexibility
A strong, mobile core distributes forces evenly during movement, preventing excessive strain on any single joint. This balanced loading protects against chronic overuse injuries.