Advanced Balance Training for Active Seniors
Safety Precautions and Considerations
Injury prevention begins with proper setup. Adjust benches to align with your knee height, position safety bars correctly, and always maintain three points of contact with machines. The first workout should focus entirely on form—many trainers recommend practicing with just a broomstick before adding weight.
Breathing technique is often overlooked but critical. Exhale during the exertion phase (when lifting), inhale during the release. This stabilizes core pressure and prevents dangerous blood pressure spikes. Those with hypertension should particularly heed this advice.
Progressive Overload and Exercise Progression
The body adapts remarkably quickly to stress. To continue seeing gains, implement the 2 for 2 rule: when you can complete two extra reps for two consecutive sessions, it's time to increase weight by 5-10%. This gradual approach prevents plateaus while minimizing injury risk.
Training logs are invaluable tools. Documenting weights, reps, and even how the movement felt creates accountability and reveals patterns. Many athletes find they make their best progress when tracking these details consistently.
Nutrition and Recovery for Optimal Results
Muscle repair requires specific building blocks. Consume 20-30g of high-quality protein within 30 minutes post-workout—this window maximizes muscle protein synthesis. Greek yogurt with berries or a whey protein shake make ideal recovery snacks.
Don't neglect micronutrients. Magnesium aids muscle relaxation, while zinc supports tissue repair. A handful of pumpkin seeds provides both, along with healthy fats. For hydration, weigh yourself before and after training—drink 16-24oz of water for every pound lost during exercise.
Incorporating Functional Movements for Daily Life
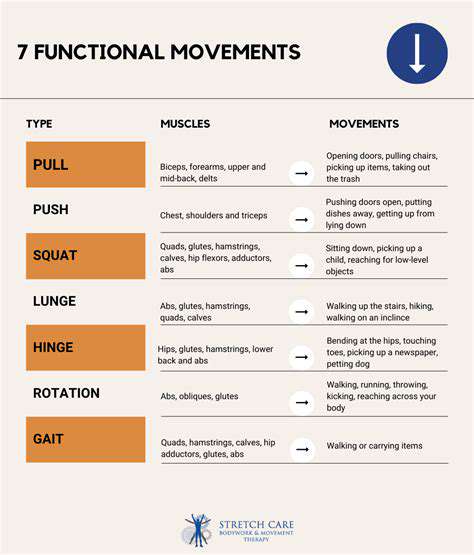
Benefits of Functional Movement
Functional training bridges the gym-life gap like no other approach. Research demonstrates that participants maintain 85% of their training gains in real-world applications, compared to just 60% with traditional workouts. This translates to tangible improvements—easier suitcase lifting, smoother garden work, and more confident stair navigation.
The neurological benefits are equally compelling. Functional movements enhance proprioception by up to 40% in older adults, significantly reducing fall risk. These exercises also promote bilateral coordination, helping counteract the one-sided dominance developed from years of habitual movements (like always carrying a purse on the same shoulder).
Examples of Functional Movements
Everyday items can become workout tools. A gallon water jug makes an excellent substitute for kettlebells—try farmer's carries to improve grip strength crucial for carrying groceries. Step-ups onto a sturdy kitchen chair mimic climbing stairs, while towel rows on a doorknob build back strength for pulling actions.
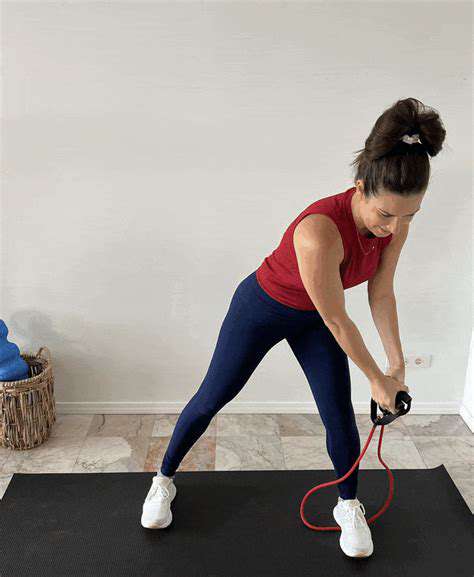
Don't overlook rotational movements. Medicine ball twists or cable rotations train the oblique muscles needed for reaching across your body—a motion used when grabbing seatbelts or turning to check blind spots while driving. These often-neglected movements prevent the weekend warrior injuries that occur during unaccustomed activities.
Integrating Functional Movements into Your Routine
Start by analyzing your daily pain points. Does your back ache after vacuuming? Incorporate deadlifts with proper hip hinge technique. Struggle with overhead luggage? Include shoulder presses in your regimen. This targeted approach yields the most immediate real-world benefits.
For time efficiency, try exercise stacking—perform a functional movement while completing another task. Do calf raises while brushing teeth, or practice single-leg stands during phone calls. These micro-workouts accumulate significant training volume without requiring extra gym time.