Energize Your Day: Morning Cardio Routine for Active Seniors
Tailoring Cardio to Senior Needs

Optimizing Exercise Intensity and Duration
Understanding the physiological changes associated with aging is crucial for tailoring cardio routines to senior needs. Reduced cardiovascular function and muscular strength often necessitate a gradual approach to exercise, prioritizing safety and avoiding overexertion. It's essential to start with shorter durations and lower intensities, gradually increasing both as fitness improves. This progressive overload principle is key to building endurance without causing injury. Monitoring heart rate and perceived exertion levels is vital to ensure the exercise remains within a safe and beneficial range. Careful consideration of individual limitations and health conditions is paramount to prevent undue stress on the cardiovascular system. This individualized approach ensures the exercise program aligns with the senior's unique needs and capabilities.
Seniors should aim for a consistent exercise routine. While the specifics will vary depending on individual health conditions, a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week is often recommended. This level of activity helps maintain cardiovascular health, improve bone density, and support overall well-being. However, it's important to emphasize that consistency is more critical than achieving these specific timeframes. A regular, albeit shorter, workout routine is often more beneficial than sporadic, intense sessions. Listening to the body and adjusting the routine accordingly is vital for long-term adherence and enjoyment.
Choosing Appropriate Cardio Activities
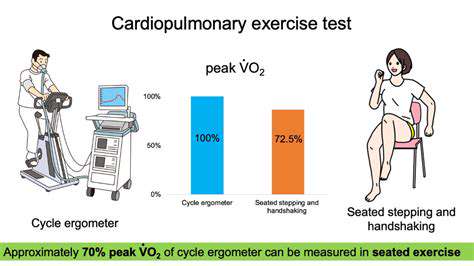
Selecting suitable cardio activities is paramount for senior fitness. Walking, swimming, and cycling are excellent options that can be easily adapted to different fitness levels and physical limitations. These activities generally have a lower impact on joints compared to running, making them suitable for individuals with arthritis or other joint issues. Water aerobics, specifically, can be particularly beneficial, providing resistance and support while reducing stress on the joints. Proper guidance from a healthcare professional or certified fitness instructor is recommended to ensure the chosen activities are safe and effective for the individual's specific needs.
Consider incorporating activities that seniors enjoy, as this enhances motivation and adherence to the exercise program. This could include dancing, chair exercises, or even brisk walking in a park. The key is finding an activity that is enjoyable and sustainable over time. Group classes and social interaction can also help to make exercise more engaging and fulfilling, fostering a sense of community and shared purpose.
Exploring various options and consulting with professionals can lead to the identification of activities that not only promote cardiovascular health but also stimulate enjoyment and motivation. This approach ensures the exercise routine aligns with the senior's preferences and life circumstances, promoting long-term adherence and positive outcomes.

Important Considerations for Senior Cardio
Warm-up Strategies
Proper warm-up routines are crucial for senior cardio, preventing injuries and preparing the body for the workout. A gradual increase in heart rate and blood flow is essential. This can involve light cardio activities like brisk walking or stationary cycling for 5-10 minutes, focusing on major muscle groups to be used during the workout. Dynamic stretching, such as arm circles, leg swings, and torso twists, is also beneficial for improving flexibility and range of motion, further reducing the risk of muscle strains or tears. These warm-up activities should be tailored to the individual's physical capabilities and limitations.
Remember, consistency is key. A daily or frequent warm-up will help maintain flexibility and prepare your body for more intense workouts as you progress. Listen to your body and adjust the intensity of the warm-up based on your individual needs and how you feel. If you experience any pain, stop immediately and consult with a healthcare professional.
Choosing the Right Cardio Exercises
Selecting appropriate cardio exercises is paramount for senior cardio routines. Low-impact exercises are generally recommended to minimize stress on joints and reduce the risk of injuries. Examples include walking, swimming, water aerobics, and stationary cycling. These activities can be adjusted in intensity and duration according to individual fitness levels and preferences. It's important to choose exercises that you enjoy and find sustainable long-term, to ensure adherence to the routine.
Consider incorporating interval training, alternating periods of high and low intensity. This method can help improve cardiovascular fitness and burn calories more effectively while minimizing the strain on joints. Consult with a healthcare professional or certified fitness trainer to determine the most suitable exercises based on your specific health conditions and limitations. Be sure to gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts over time.
Monitoring Heart Rate and Resting Periods
Monitoring heart rate during cardio sessions is a vital aspect of senior cardio routines. Knowing your target heart rate zone can help ensure you're working out effectively without overexerting yourself. It's generally recommended to keep track of your heart rate and make necessary adjustments to the intensity and duration of the workout as needed. Consult with your doctor to determine the appropriate target heart rate zone for your age and health condition. This information will guide you in creating a safe and effective workout routine.
Adequate rest and recovery periods are equally important. Allowing your body to recover between workouts is crucial for muscle repair and preventing fatigue. Listen to your body and take rest days when needed. Adjusting the duration and intensity of your workouts based on your body's response will optimize your performance and minimize the risk of injuries or overtraining. Don't hesitate to seek advice from a healthcare professional or fitness expert if you have any concerns.
Nutrition and Hydration
Proper nutrition and hydration are fundamental for supporting senior cardio routines. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains provides the necessary nutrients for energy production and muscle repair. Staying adequately hydrated is equally important, as dehydration can negatively impact cardiovascular health and exercise performance. Drinking plenty of water before, during, and after your workouts is crucial to maintain optimal hydration levels.
Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise is also important for overall health and well-being. A registered dietitian or nutritionist can offer personalized dietary advice to support your cardio routine. A healthy diet combined with regular exercise can greatly enhance the effectiveness of your cardio workout routine. Remember to listen to your body and adjust your diet and hydration as needed to maintain optimal health and energy levels.