Preventing Falls: Balance Exercises for Seniors of All Ages
The Importance of Balance for Seniors

Finding Harmony in Artistic Expression
Mastering balance in artistic creation represents a fundamental skill for crafting visually compelling works. Beyond mere symmetry, it requires a nuanced grasp of how colors, shapes, lines, and textures interact. A well-balanced piece naturally directs the observer's gaze, establishing visual harmony and engagement. Artists utilize multiple methods to accomplish this equilibrium, including strategic placement of elements and thoughtful use of empty space. Through these techniques, creators can more effectively convey their message and elicit specific emotional reactions from their audience.
Artistic balance transcends visual components. It represents a careful calibration between concept and execution, between emotional expression and technical skill, and between the artist's vision and viewer perception. This multidimensional approach to balance creates richer artistic experiences that resonate more deeply with audiences. When all these elements harmonize, the artwork achieves a powerful impact that lingers with the viewer.
The Role of Balance in Various Art Forms
Balance serves as a foundational principle across all artistic media. Painters achieve it through color distribution and compositional arrangement, while sculptors manipulate form and space to create equilibrium. Photographers establish balance through framing choices and lighting techniques. This universal principle connects diverse creative disciplines, serving as a common language of visual organization. Whether working in traditional or digital media, artists who understand balance create more compelling and coherent works.
The concept extends beyond physical composition to emotional impact. Properly balanced works often evoke feelings of stability and satisfaction, while imbalance can create tension or unease. Skillful application of balance principles allows artists to craft pieces that are both visually striking and emotionally powerful, facilitating deeper connections with their audience. In musical composition, balance appears in instrumentation and dynamics; in literature, it manifests through narrative structure and thematic development. This principle remains equally vital in design fields and architectural practice.
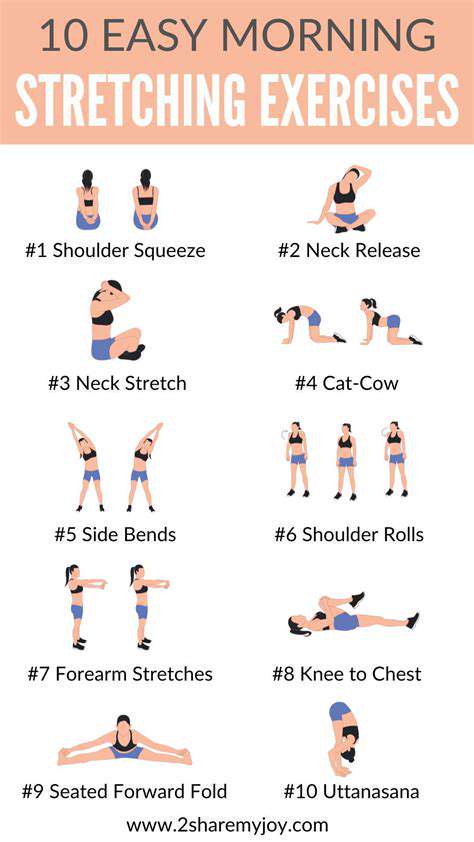
Simple Exercises to Enhance Balance
Basic Standing Movements
Standing exercises offer excellent benefits for improving stability and reducing fall risk. These movements strengthen leg and core muscles while enhancing spatial awareness. Begin with feet positioned comfortably apart, maintaining proper spinal alignment and engaged abdominal muscles. Perform these exercises in a clear, safe space to prevent accidents.
The tandem walk proves particularly effective - place one foot directly in front of the other as if walking on a tightrope. This movement strengthens ankle and foot muscles critical for stability. Complete 10-15 steps in each direction. Single-leg stands also provide significant benefits. Lift one foot slightly off the ground, hold briefly, then switch sides. Regular practice of 3 sets per side yields optimal results.
Supported Seated Exercises
For those needing additional support, chair-based exercises offer a safe alternative. Select a sturdy, stable chair and sit upright with feet flat. Extend one leg forward, hold momentarily, then lower and repeat with the opposite leg. These movements build lower body strength while maintaining safety.
Chair stands represent another valuable option. From a seated position, push through the heels to rise, pause briefly standing, then control the return to sitting. This functional movement improves ability to transition between positions safely. Perform 10 controlled repetitions.
Lateral Movement Drills
Side-stepping exercises develop coordination and stability. Stand with feet comfortably apart, then step sideways while maintaining posture. Bring the trailing foot to meet the leading foot and repeat. These movements strengthen hip stabilizers important for preventing falls. Focus on smooth, controlled motions throughout.
Instability Training
Balance boards provide progressive challenges for stability training. Begin with basic standing on the unstable surface, progressing to more complex movements as ability improves. This equipment enhances proprioception - the body's awareness of its position in space. Start with short sessions and gradually increase difficulty.
Inner Ear Conditioning
Vestibular exercises improve the balance system located in the inner ear. Simple head turns while maintaining posture or eyes-closed standing can enhance this system's function. Perform these exercises in safe environments with support available if needed, as they intentionally challenge the balance system.
Customizing Exercises for Individual Requirements

Strength-Building Modifications
Targeted strength training focuses on muscle groups essential for stability and functional movement. Proper body alignment plays a critical role in movement efficiency and injury prevention. Exercises like modified planks and controlled lifts, when performed with correct form, develop core stability and postural support.
Progressive resistance training using elastic bands or light weights builds necessary strength without excessive strain. This approach ensures safe development of muscles needed for daily activities and specialized movements.
Flexibility Adaptations
Maintaining mobility prevents stiffness and supports proper body mechanics. Focused stretching of major muscle groups, particularly those prone to tightness, preserves range of motion. Regular flexibility work reduces discomfort during prolonged activities and prevents overuse injuries.
Dynamic stretching as part of warm-up routines prepares the body for activity while improving functional flexibility. This approach reduces injury risk and enhances movement quality.
Coordination Development
Precision movements require well-developed hand-eye coordination. Activities involving small object manipulation or tool use can significantly improve this skill. Regular practice of coordinated movements enhances ability to perform detailed tasks accurately.
Simple coordination drills using common objects can improve dexterity and control. Consistent practice leads to noticeable improvement in performing complex movements.
Postural Training
Maintaining proper alignment during activities prevents strain and fatigue. Discipline-specific postural exercises, including modified yoga and stabilization work, support healthy movement patterns. Conscious attention to posture prevents common overuse injuries associated with repetitive motions.
Hand and Wrist Care
Protecting these vulnerable areas requires regular conditioning. Specific exercises maintain strength and flexibility in hands and wrists. Proactive care prevents common repetitive stress conditions that can limit functionality. Incorporating these exercises preserves long-term hand health and performance.
Environmental Adjustments and Safety Measures
Home Modifications for Safety
Home environment adjustments dramatically decrease fall hazards. Eliminate potential tripping dangers like loose floor coverings and electrical cords. Install sufficient lighting, particularly in transition areas and stairwells. Safety bars in bathrooms provide essential support in slippery conditions. Elevated toilet seats and textured bath mats further reduce risks in wet areas. These practical modifications create a safer living environment.
Proper footwear selection also contributes to safety. Choose shoes with good traction and support for indoor and outdoor use. Ensure stairways have secure railings and adequate lighting. Keeping walkways clear of obstructions enhances safety in frequently used areas. These thoughtful changes help create a home environment that supports stability.
Daily Activity Precautions
Mindful movement during routine tasks prevents accidents. Rise slowly from seated positions, using available supports. Maintain awareness of surroundings and avoid hurried movements. Assistive devices like walking aids provide valuable stability when needed.
Exercise particular caution on stairs. Always use handrails and proceed deliberately. Ensure adequate lighting and watch for potential obstacles like pets. Consistent application of these precautions significantly reduces daily fall risks.
Special Considerations for High-Risk Individuals
Those with specific health challenges require tailored safety approaches. Environmental modifications, proper assistive devices, and professional guidance address individual needs. Healthcare provider consultations identify and manage conditions affecting balance.
Regular medical check-ups monitor conditions that may impact stability. Personalized exercise programs designed by professionals improve strength and coordination. Appropriate mobility aids and professional advice enhance safety for those with movement challenges.
Maintaining Physical Condition
Regular balance and strength exercises form the foundation of fall prevention. Targeted workouts improve coordination, flexibility, and stability. Even brief daily sessions provide meaningful benefits. Simple exercises like single-leg stands and controlled walking patterns enhance balance.
Structured physical therapy programs offer customized approaches to improving stability. Consistent physical activity remains crucial for comprehensive fall prevention. Maintaining mobility through regular exercise significantly reduces fall risks.