Balance Training for Seniors with Peripheral Neuropathy
Promoting Safety and Preventing Falls
Importance of Balance Training
Maintaining balance is crucial for seniors, as falls are a leading cause of injuries and disability. Balance training exercises, tailored to individual needs and abilities, can significantly reduce the risk of falls. These exercises strengthen the muscles that support the body and improve proprioception, which is the body's awareness of its position in space. By improving these areas, seniors can enhance their stability and confidence in everyday activities.
Regular balance training can lead to improvements in gait, posture, and coordination, all of which are essential for preventing falls. A proactive approach to balance training empowers seniors to maintain their independence and quality of life.
Identifying Risk Factors for Falls
Understanding the potential risk factors for falls is the first step in creating a personalized balance training program. Age-related changes, such as muscle weakness, vision impairment, and reduced bone density, can increase the risk of falls. Medications, certain medical conditions, and environmental hazards, such as uneven surfaces or poor lighting, also contribute to the likelihood of falling. A thorough assessment by a healthcare professional can help identify specific risk factors for each individual.
Exercises for Improved Balance
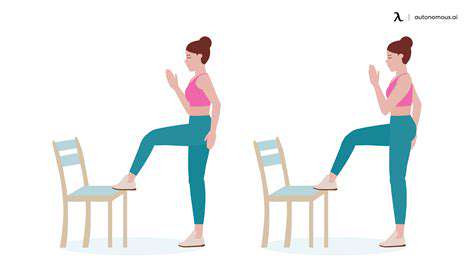
Numerous exercises can be incorporated into a balance training routine. Simple exercises like standing on one leg, heel-to-toe walking, and performing chair stands can improve leg strength and balance. More advanced exercises, such as Tai Chi and Yoga, can provide a holistic approach to balance improvement. It's crucial to start slowly and gradually increase the difficulty of the exercises as strength and stability improve.
These exercises should be tailored to the individual's specific needs and abilities. Consult with a physical therapist or healthcare professional to develop a safe and effective exercise program that addresses individual risk factors.
The Role of Vision and Hearing in Balance
Vision and hearing play a vital role in maintaining balance. Changes in vision, such as decreased visual acuity or depth perception, can significantly impact balance and increase the risk of falls. Similarly, hearing problems can affect spatial awareness and coordination, further increasing the risk. Addressing vision and hearing issues through regular checkups and appropriate assistive devices can significantly improve balance.
Environmental Modifications for Fall Prevention
Creating a safe and supportive environment is just as important as physical exercises. Removing tripping hazards, such as loose rugs or cords, and improving lighting conditions can reduce the risk of falls. Installing grab bars in bathrooms and hallways, providing adequate lighting, and using non-slip mats can enhance safety and reduce the likelihood of falls. Adapting the home environment to suit the needs of the elderly is crucial in fall prevention.
Working with Healthcare Professionals
Collaboration with healthcare professionals is essential in developing a comprehensive balance training program. Physical therapists, occupational therapists, and doctors can provide personalized assessments, exercise recommendations, and guidance on fall prevention strategies. Regular checkups and consultations with these professionals can help monitor progress, address any emerging issues, and ensure the safety and effectiveness of the balance training program. They can also provide valuable advice on medication management and other factors that may affect balance.