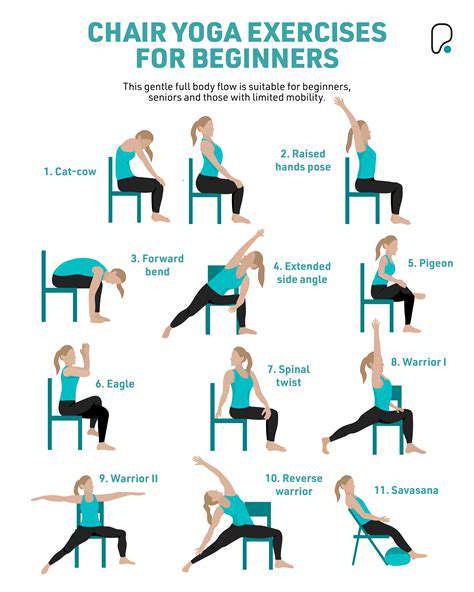
Exercises to Improve Posture for Older Adults
Understanding Core Muscles
Core muscles are a group of muscles located deep within the abdomen and back, encompassing the transverse abdominis, rectus abdominis, obliques, and erector spinae. These muscles work together to stabilize the spine, maintain posture, and support the body during movement. Proper core engagement is crucial for preventing back pain and promoting overall physical well-being. Understanding their function and importance is the first step towards developing a strong and healthy core.
The Importance of Core Strength for Posture
A strong core provides a stable foundation for the spine, allowing for correct posture. When core muscles are weak, the spine is more susceptible to slouching, rounding, or other postural deviations. This can lead to discomfort, pain, and even long-term musculoskeletal issues. Strengthening these muscles helps maintain an upright posture, reducing stress on the back and promoting a more balanced body alignment.
Common Core Exercises for Posture Improvement
Numerous exercises can effectively target core muscles. Planks, crunches, and bridges are popular choices, but variations and modifications are essential to ensure proper form and avoid injury. Focus on controlled movements and engaging the core muscles throughout each repetition to maximize effectiveness. Proper form is critical to prevent strain and ensure that the exercises are working the intended muscles.
Benefits Beyond Posture: Improved Balance and Stability
A strong core translates to improved balance and stability. These muscles play a vital role in coordinating movements and maintaining equilibrium, which is crucial for everyday activities like walking, running, and even simple tasks. Improved balance reduces the risk of falls, especially as we age, and enhances athletic performance by providing a solid base for movement.
Progressive Overload for Maximum Results
To continue seeing progress, it's crucial to progressively overload the core muscles. This means gradually increasing the intensity, duration, or difficulty of your exercises over time. This could involve adding more repetitions, increasing the resistance, or holding a plank for a longer duration. Constant challenges keep the core muscles working harder, leading to greater strength and endurance.
Incorporating Core Work into Your Routine
Integrating core exercises into your daily or weekly routine is essential for long-term improvement. Even short, focused workouts can yield significant benefits. Aim for at least 2-3 sessions a week, incorporating core work into your existing fitness regimen or creating dedicated time slots. Consistency is key to building a strong and resilient core.
Addressing Potential Challenges and Considerations
While strengthening core muscles is beneficial, it's important to address potential challenges. Consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have pre-existing conditions or injuries. Listen to your body, and modify exercises as needed to avoid pain or discomfort. Focusing on proper form and gradual progression is essential to avoid injury and achieve optimal results.

Balance and Coordination Exercises: Preventing Falls
Importance of Balance and Coordination
Maintaining balance and coordination is crucial for preventing falls, especially as we age. Loss of balance can lead to serious injuries, impacting mobility and independence. Simple exercises can significantly improve these essential functions, reducing the risk of falls and promoting a healthier, more active lifestyle. By strengthening muscles and improving proprioception (the body's awareness of its position in space), we can enhance our stability and responsiveness.
Regular practice of balance and coordination exercises can have a profound impact on our overall well-being. These exercises are not just for older adults; individuals of all ages can benefit from incorporating them into their routine. Improving balance and coordination can enhance athletic performance, reduce the risk of injuries in daily activities, and improve overall quality of life.
Simple Exercises for Improved Balance
Many simple exercises can be performed at home to improve balance. Standing on one leg, either with or without support, is a great starting point. Heel-to-toe walking, or tandem walking, is another effective exercise that challenges your balance. Try closing your eyes while standing on one leg to further increase the difficulty and engage your proprioceptive senses.
Incorporating these exercises into your daily routine, even for a few minutes, can make a significant difference. Consistency is key to seeing improvement in balance and coordination over time. Remember to perform these exercises slowly and with proper form to avoid injuries.
Coordination Exercises Using Everyday Objects
Simple household items can be used to enhance coordination exercises. Picking up small objects from the floor, tossing a ball, or even playing with stress balls can engage different muscle groups and improve hand-eye coordination. These activities are fun and engaging, making it easier to incorporate them into a daily routine.
Using everyday objects can provide a fun and engaging approach to improving coordination. This makes it easier to stay motivated and consistent with the exercise routine. Gradually increase the difficulty of these tasks as you improve your coordination, challenging your body in new ways.
Advanced Balance Exercises
As balance improves, you can progress to more challenging exercises. Single-leg squats, or using a balance board, are examples of advanced exercises. These exercises require greater stability and focus, further strengthening the muscles responsible for maintaining balance.
Advanced exercises are important for individuals who want to take their balance and coordination to the next level. They can help prevent falls, reduce the risk of injuries, and improve overall athletic performance. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program, especially if you have any underlying health conditions.
Exercises for Specific Balance Challenges
Certain balance challenges, such as dizziness or vertigo, may require specialized exercises. These exercises are designed to address the specific needs of individuals experiencing these conditions. Consulting with a physical therapist is crucial for developing a personalized exercise plan to help manage these challenges effectively.
A physical therapist can assess your specific balance challenges and create a tailored exercise program. This approach ensures that the exercises are safe and effective for your individual needs, minimizing the risk of further complications. Following a personalized plan, guided by a professional, is key to achieving the best possible results in addressing specific balance concerns.
The Role of Proprioception in Balance
Proprioception, the body's internal sense of position and movement, plays a critical role in maintaining balance. Exercises that challenge proprioception, such as standing on uneven surfaces or performing exercises with eyes closed, can significantly improve balance and coordination.
Understanding and training proprioception is essential for improving balance. By engaging these internal awareness mechanisms, the body learns to better respond to changes in posture and position, reducing the risk of falls and promoting a more stable and responsive system. Engaging in exercises that challenge proprioception strengthens this critical aspect of balance control.
Incorporating Balance and Coordination Exercises into Your Routine
Incorporating balance and coordination exercises into your daily routine doesn't require a lot of time or specialized equipment. Even simple activities like walking up and down stairs or standing on one leg while brushing your teeth can be beneficial. Finding ways to incorporate these exercises into your existing routines will help you stay motivated and consistent in your efforts to improve balance and coordination.
Making these exercises a part of your routine is key to long-term success. Scheduling dedicated time for these activities can help create a consistent habit. Consider incorporating them into your morning routine, before meals, or even as a part of your commute. Finding ways to integrate them seamlessly into your daily life makes them more manageable and sustainable.