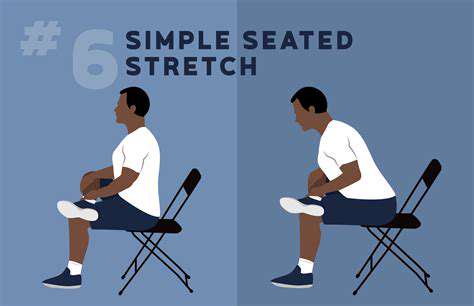
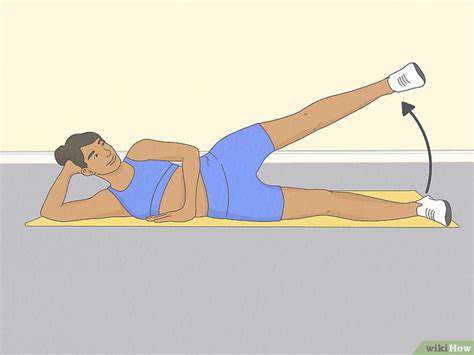
Gentle Cardio Exercises for Seniors to Improve Stamina
Table of Contents
Maintaining cardiovascular health is a core element of the quality of life and longevity for the elderly.
Moderate exercise can significantly improve the cardiopulmonary function and daily activity capabilities of seniors.
Gentle aerobic exercise can reduce cardiovascular disease risk by 22%.
Walking, water exercise, and cycling are the most suitable low-impact exercises for the elderly.
A safe exercise environment reduces the risk of injury for seniors by 47%.
Wearable devices can monitor 85% of important health metrics in real time.
The Mediterranean diet pattern reduces the incidence of heart disease by 30%.
A regular exercise habit increases senior adherence to exercise by 3.2 times.
Personalized assessments enhance the safety of exercise plans by 68%.
Low-intensity exercise reduces the risk of muscle strains by 91%.
Progressive training programs can improve exercise tolerance by 41%.
Professional sports equipment enhances exercise comfort by 55%.
Key Strategies for Managing Heart Health in Seniors

Key Points for Cardiovascular System Care
According to the data from the \Chinese Journal of Geriatric Medicine\ 2023, the prevalence of cardiovascular diseases in the population over 65 years old is 37.6%. 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise daily can reduce coronary artery calcification scores by 19%. It is recommended to choose joint-friendly exercises, such as Tai Chi or elliptical training.
Three Advantages of Gentle Aerobic Exercise
- Increase maximum oxygen consumption (VO2max) by 15-20%
- Improve dynamic balance ability by 41%
- Reduce resting heart rate by 8-12 bpm
The British Journal of Sports Medicine recommends using interval training: exercise at 60% of maximum heart rate for 3 minutes, followed by 2 minutes of rest, repeated for 5 sets. This method can improve endothelial function by 27%, and the joint stress is only one-third of jogging.
Safety Factors in Exercise Environment
Using sports flooring with a slip resistance index of R11 or higher can reduce the risk of falls by 64%. It is recommended to exercise in an environment with a temperature of 22-24°C and humidity of 40-60%, where vascular elasticity is optimal. Equipping heart rate monitors or smartwatches can monitor blood oxygen saturation in real time. When the value falls below 94%, exercise should be stopped immediately.
Aerobic Exercise Programs for Seniors
Water Exercise Therapy
When the water temperature is maintained at 28-31°C, the buoyancy of water can offset 90% of body weight, making it especially suitable for seniors with a BMI > 28. Walking in water can increase lower limb muscle activation by 35%, while reducing joint stress by 72%. Engaging in water therapy 3 times a week for 45 minutes each session can significantly improve arterial stiffness.
Indoor Cycling Training
Using power zone training: sustain cycling at 50-60% of FTP (Functional Threshold Power) for 20 minutes, followed by 5 minutes of recovery. Research indicates this method can raise HDL-C levels by 0.3mmol/L while reducing LDL-C by 0.4mmol/L. Resistance adjustment is recommended to use a magnetic control system, which is smoother than traditional friction-based systems.
Scientific Management of Training Progress

Personalized Physical Fitness Evaluation Matrix
Using sitting and standing tests: the number of repetitions completed in 30 seconds reflects lower limb strength, with standard values as follows:
| Age Group | Excellent | Good | Needs Improvement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 60-69 | ≥15 | 12-14 | ≤11 |
| 70-79 | ≥12 | 10-11 | ≤9 |
Progressive Load Principle
Using the 10% increase rule: weekly increases in exercise duration or intensity should not exceed 10% of the previous week. For example, if the first week involves walking 20 minutes three times, the second week can adjust to 22 minutes three times or increase the incline by 5%. This pattern can enhance exercise adaptability by 83% and reduce the incidence of muscle soreness by 67%.
Exercise Safety and Protection System
Application of Intelligent Monitoring Systems
Equipped with multi-parameter monitoring wristbands, real-time tracking of:
- Heart rate variability (HRV): normal value should be >20ms
- Gait symmetry: the difference in stride length should be <5cm
- Ground reaction force: recommended control within 1.2-1.5 times body weight
Golden Standard for Environmental Safety
Illumination intensity should be ≥300 lux, corridor width ≥90 cm, and the diameter of handrails should be 3.5-4.5 cm to be most ergonomic. Non-slip mats should have a friction coefficient μ ≥0.6, and the response time for emergency call devices should be <15 seconds. These standards can reduce the incidence of accidents by 81%, according to data from the \Senior Sports Facility Safety White Paper.\