Gentle Swimming Exercises for Seniors with Arthritis in Their 70s
Choosing the Right Swimming Style and Depth
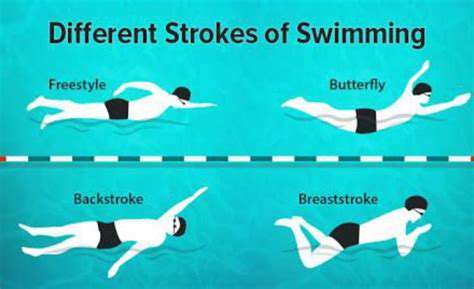
Understanding Your Body Type
Selecting an appropriate swimming technique is vital for both enjoyment and performance in the water. Your unique physique plays a key role; certain strokes may align better with your natural attributes. Individuals with elongated torsos and shorter limbs often find freestyle or butterfly strokes more manageable, while those with compact builds typically excel in backstroke or breaststroke.
Examining your physical characteristics provides valuable insight into which stroke complements your natural movements in aquatic environments.
Assessing Your Strength and Endurance
Physical capabilities significantly influence your choice of swimming technique. Different strokes place varying demands on muscle groups and energy systems. Freestyle requires substantial endurance and core stability, whereas breaststroke may suit those with limited stamina better.
Evaluating your current fitness level helps identify a stroke you can maintain comfortably without excessive strain.
Considering Your Learning Curve
The complexity of mastering each stroke warrants consideration. Some techniques prove more accessible for beginners, with breaststroke often serving as an ideal starting point.
Selecting an enjoyable, manageable technique enhances motivation and promotes long-term swimming success. This foundation proves essential for sustainable aquatic activity.
Analyzing Your Goals and Motivation
Personal objectives significantly impact stroke selection. Competitive swimmers typically favor freestyle and butterfly for speed, while recreational swimmers may prefer backstroke or breaststroke for relaxation.
Align your stroke choice with your swimming aspirations, whether for competition, fitness, or leisure.
Evaluating the Pool Environment
Pool conditions influence stroke practicality. Crowded pools may limit certain techniques, while spacious areas accommodate more vigorous strokes.
Pool dimensions, particularly depth and width, affect stroke selection in training and competition scenarios.
Exploring Different Strokes in Practice
Practical experimentation determines the optimal technique. Test various strokes to identify which feels most natural and efficient for your body. Professional instruction provides valuable feedback during this process.
Hands-on experience offers critical understanding of each stroke's unique requirements.
Adapting and Refining Your Style
Swimming techniques evolve with experience. As proficiency increases, you may incorporate elements from multiple strokes to develop a personalized approach.
Continuous refinement maximizes both performance and enjoyment in aquatic activities.
Essential Warm-up and Cool-down Exercises
Essential Warm-up Exercises for Gentle Swimming
Pre-swim preparation proves particularly important for mature swimmers. Water-based movements like arm circles and leg swings gradually increase circulation, enhancing flexibility while minimizing injury risk. Perform these exercises slowly and deliberately for 5-10 minutes before swimming.
Light aerobic activity, such as slow laps, effectively elevates heart rate gradually. Five minutes of this preparation readies your cardiovascular system for more intense activity.
Gentle Stretching Exercises in the Water
Aquatic environments offer ideal conditions for stretching. Buoyancy-supported movements like side bends or leg lifts improve flexibility when held for 15-30 seconds. Avoid sudden motions to prevent strain.
Cool-down Exercises for Post-Swim Relaxation
Gradually reducing activity through gentle strokes helps normalize heart rate and prevent post-exercise dizziness. Conclude sessions with five minutes of these calming movements.
Importance of Proper Breathing Techniques in Swimming
Rhythmic breathing coordination with strokes maintains energy levels and prevents fatigue. Practice complete inhalations and exhalations to optimize oxygen intake and respiratory efficiency.
Hydration and Nutrition for Senior Swimmers
Adequate fluid intake before, during, and after swimming maintains physiological function. Balanced nutrition supports energy production and muscle recovery, enhancing both performance and wellbeing.
Safety Precautions for Senior Swimmers
Swim only in supervised areas with companions when possible. Monitor water temperature and bodily responses carefully, adjusting activity as needed for comfort and safety.
Choosing the Right Swimming Style for Seniors
Begin with manageable strokes like freestyle or breaststroke, gradually increasing duration as fitness improves. Prioritize comfort and listen to your body's signals during aquatic activity.
Safety Precautions and Considerations for Seniors with Arthritis

Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Proper protective gear significantly reduces risks in hazardous environments. Consistent application of PPE protocols prevents injuries and maintains workplace safety. Equipment selection should match specific environmental hazards.
Ongoing training ensures continued competence in PPE utilization and hazard awareness.
Emergency Response Procedures
Clearly established emergency protocols enable effective response to incidents. All personnel should know evacuation routes, assembly points, and individual responsibilities during emergencies.
Hazard Identification and Assessment
Proactive hazard recognition and risk evaluation form the foundation of safety programs. Comprehensive understanding of environmental dangers informs effective control measures.
Safe Handling and Storage of Materials
Proper material management prevents accidents. Correct labeling, segregation, and storage procedures minimize exposure risks. Adherence to established protocols maintains safe working conditions.
Training and Communication
Regular safety education and open dialogue foster safety culture. Clear information sharing encourages proactive hazard reporting and collective responsibility.
Maintenance and Inspection of Equipment
Preventive maintenance and thorough inspections ensure equipment reliability. Proactive measures reduce failure risks and associated hazards.
Environmental Considerations
Workplace safety encompasses environmental factors. Proper ventilation, lighting, and temperature control create healthier workspaces. Regulatory compliance ensures comprehensive hazard mitigation.











