Advanced Balance Techniques for Active Older Adults
Nutrition and Lifestyle Factors for Optimal Balance
Dietary Support for Stability
Nutritional balance significantly influences overall health and consequently, physical stability. Consuming foods abundant in key nutrients like calcium, vitamin D, and magnesium supports bone and muscle integrity. These nutrients directly relate to stability and coordination, decreasing fall risk while enhancing body position awareness. Including calcium-rich dairy, dark leafy greens, and fortified foods contributes substantially to skeletal health. Adequate protein consumption similarly supports muscle maintenance and development - fundamental components of stability.
Beyond specific nutrients, overall dietary quality matters. Diets emphasizing fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provide diverse vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants supporting immune function and reducing inflammation. Chronic inflammation can negatively impact various physiological processes, including those related to stability. Minimizing processed foods, sugary beverages, and excessive unhealthy fats similarly supports optimal stability and general wellbeing.
Fluid Balance and Stability
Proper hydration, frequently underestimated, significantly impacts stability. Water facilitates numerous physiological processes including nutrient transport, joint lubrication, and temperature regulation. Dehydration can result in fatigue, dizziness, and diminished muscular function - all potentially compromising stability. Maintaining adequate hydration throughout the day proves essential, particularly during physical exertion or in warm environments. Carrying a water container and consuming fluids regularly helps maintain optimal hydration status.
Lifestyle Considerations for Enhanced Stability
Beyond nutrition, specific lifestyle choices substantially influence stability. Regular physical activity incorporating strength, flexibility, and coordination exercises remains paramount. Practices like yoga, tai chi, and Pilates offer particular benefits for stability and body awareness. These disciplines improve muscular strength, joint mobility, and movement coordination, thereby reducing fall risk and enhancing stability control.
Sufficient sleep represents another critical lifestyle factor. During sleep, the body undergoes repair processes affecting tissues and neural pathways involved in stability maintenance. Striving for 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly allows for proper physiological recovery. Stress reduction techniques including meditation, controlled breathing, or nature exposure may also improve stability by mitigating stress hormone effects that can impair various bodily functions.
Exercise for Sustained Stability
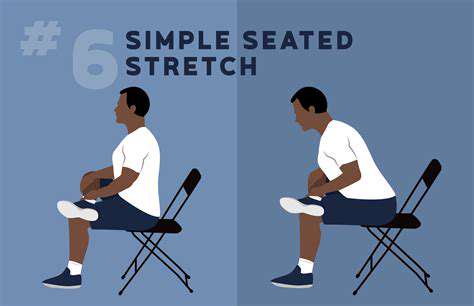
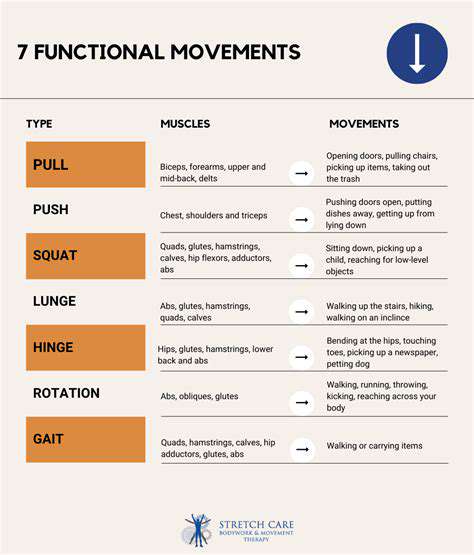
Regular physical activity remains essential for maintaining stability and preventing falls, particularly with advancing age. Exercises targeting stability, strength, and flexibility prove most beneficial. Incorporating resistance training like squats, lunges, and calf raises significantly strengthens leg and core muscles crucial for stability maintenance. Specific stability exercises including tandem walking, single-leg standing, or controlled standing toe raises directly challenge the body's stability mechanisms and enhance body awareness. Combining these with stretching improves flexibility, important for maintaining stability and movement range.
Consider incorporating activities that progressively challenge stability, such as walking on varied surfaces or incorporating stability balls into exercises. These activities enhance the body's adaptive capacity to maintain equilibrium. Always consult healthcare providers or physical therapists before initiating new exercise programs, particularly with pre-existing medical conditions.